If you're searching for "Google Jobs API", here's the quick answer: Google has discontinued the Jobs API. But you can still get your job listings to appear on Google for Jobs by using two main methods:
- Structured Data with JobPosting Schema (JSON-LD): Add structured data to your job listing pages, so Google can understand key details like job title, location, and salary.
- XML Sitemaps + Google Indexing API: Use XML sitemaps to help Google discover your job listings and the Indexing API for instant updates when jobs are added or removed.
These approaches ensure your job postings are visible in Google Search results, driving more traffic to your site. Below, you'll find step-by-step guidance on implementing each method and avoiding common mistakes.
What People Actually Want When Searching for Google Jobs API
When you search for "Google Jobs API", what you're really looking for is a way to get your job listings to show up in Google for Jobs. But here's the catch: there isn’t a traditional API for this. Instead, Google relies on properly formatted job listings that its systems can discover and display. This shift - from pushing data through an API to pulling data via structured markup - has changed how job listings are distributed on Google. It’s all about integrating your listings methodically to make sure they’re noticed.
What Is Google for Jobs?
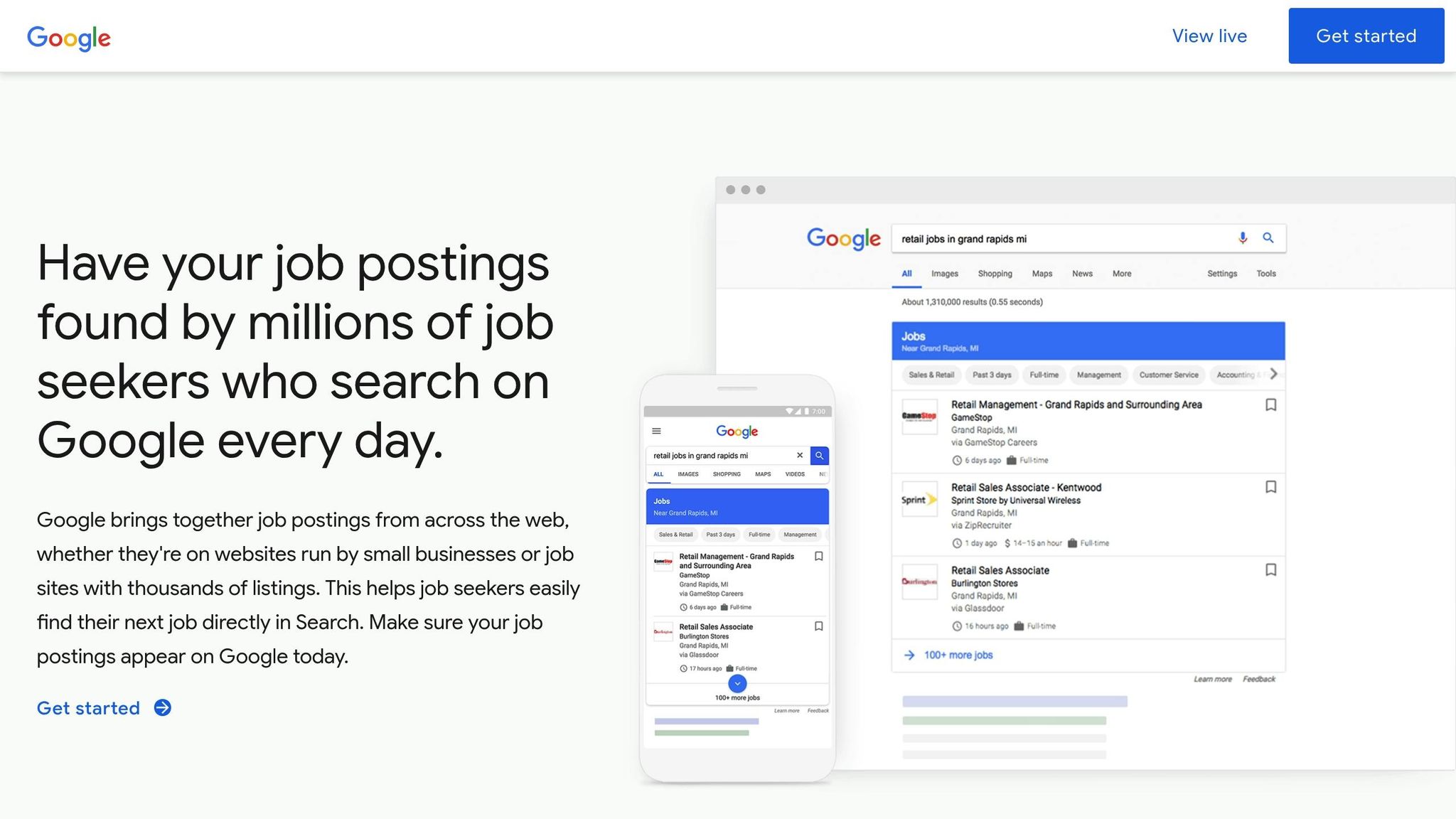
Google for Jobs is a feature within Google Search that organizes and displays job listings right in the search results. For example, if someone searches for "software engineer jobs in Austin" or "remote marketing positions", they’ll see a dedicated section filled with job postings pulled from company websites, job boards, and recruitment platforms.
For job seekers, it’s a game-changer. They get a streamlined interface with filters for location, salary, job type, and posting date - all in one place. On the other hand, employers and job boards gain increased visibility without having to spend on paid ads. Plus, this integration can improve your website’s overall SEO, potentially boosting its performance in other types of searches as well.
Google identifies these job postings by scanning websites for structured data. If your job listings are formatted correctly, they’ll get picked up and displayed in Google for Jobs.
Why Integration Methods Matter More Than APIs
The way you integrate your job listings with Google for Jobs is critical for maintaining visibility. The two main methods to ensure your listings appear are:
- Structured data using JSON-LD: This involves using the JobPosting schema to mark up your job listings.
- XML sitemaps: These help Google discover your job postings, especially when paired with the Google Indexing API for quicker updates.
These methods are reliable, thoroughly documented, and give you long-term control over how your listings are indexed and displayed. As Google’s requirements and algorithms evolve, understanding these integration techniques - and using tools like Google Search Console to resolve indexing issues - will help keep your job listings visible and competitive.
Method 1: Adding Structured Data with JSON-LD
Structured data is the backbone of getting your job listings featured on Google for Jobs. It provides a standardized way for Google to understand and display your job postings accurately, acting as a bridge between your job board and Google's search engine.
What Is Structured Data?
Structured data uses specific markup to help search engines interpret and organize key details like job title, company, location, salary, and description. For job listings, it ensures Google can easily identify and display your postings. Without this markup, your job listings might not appear in Google for Jobs.
Google recommends using JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) for structured data. Unlike microdata or RDFa, JSON-LD consolidates all job-related information into a single block of code, usually placed in the <head> section of your webpage. This method minimizes errors and ensures Google processes your data correctly. To optimize your listings, it's essential to include the required fields in the JobPosting schema.
JobPosting Schema: Required Fields and Recommendations
The JobPosting schema includes mandatory fields that Google needs to display your job listings. Missing any of these fields can prevent your job from appearing in search results.
Here are the required fields:
- title: The name of the job position.
- description: A detailed explanation of the role (Google advises at least 600 characters).
- hiringOrganization: The name of the company offering the job.
- jobLocation: The location of the job.
- employmentType: Specifies if the role is full-time, part-time, contract, etc.
- validThrough: The expiration date of the job posting.
The validThrough field is critical - it tells Google whether the job is still active. Adding optional fields like baseSalary, jobBenefits, workHours, educationRequirements, experienceRequirements, skills, and applicantLocationRequirements can improve click-through rates by 20–40%. These details give potential candidates the extra context they need to decide if the job is a good fit.
How to Add JSON-LD to Your Job Listings
The way you implement JSON-LD depends on whether your job listings are static or dynamic. For static pages, you can manually add JSON-LD code to the HTML of each job posting. For dynamic listings that frequently change, you'll need to generate the code programmatically based on your job data.
Here’s a complete example of JSON-LD markup for a job posting:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org/",
"@type": "JobPosting",
"title": "Senior Software Engineer",
"description": "We are seeking a Senior Software Engineer to join our growing team. You will work on scalable backend systems, mentor junior developers, and contribute to architectural decisions. Required: 5+ years of experience with Python or Java, experience with cloud platforms (AWS/GCP), and strong system design skills.",
"hiringOrganization": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "TechCorp Inc.",
"sameAs": "https://www.techcorp.com",
"logo": "https://www.techcorp.com/logo.png"
},
"jobLocation": {
"@type": "Place",
"address": {
"@type": "PostalAddress",
"streetAddress": "123 Tech Boulevard",
"addressLocality": "San Francisco",
"addressRegion": "CA",
"postalCode": "94105",
"addressCountry": "US"
}
},
"baseSalary": {
"@type": "PriceSpecification",
"priceCurrency": "USD",
"price": "150000",
"priceComponentType": "https://schema.org/SalaryTypeAnnual"
},
"employmentType": "FULL_TIME",
"datePosted": "2025-12-03",
"validThrough": "2026-01-31T23:59:59Z",
"applicantLocationRequirements": {
"@type": "Country",
"name": "US"
}
}
In this example:
- @context and @type define the schema as JobPosting.
- hiringOrganization includes the company's name, website, and logo.
- jobLocation uses a structured PostalAddress for clarity.
- baseSalary specifies the annual salary in USD.
- Fields like employmentType, datePosted, and validThrough provide key details about the job.
To add this code to your job posting, place it within a <script> tag in the <head> section of your HTML:
<head>
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org/",
"@type": "JobPosting",
// ... rest of your JSON-LD code
}
</script>
</head>
Before publishing, use Google's Rich Results Test tool to verify that your implementation is correct and that Google can read your job posting.
For job boards managing multiple listings, platforms like Job Boardly provide automated solutions with built-in Google Jobs integration. However, understanding the basics of JSON-LD can help you troubleshoot and refine your listings for better visibility.
Method 2: Using XML Sitemaps and Google Indexing API

XML sitemaps and the Google Indexing API are powerful tools to ensure Google discovers and indexes your job listings quickly. These methods help streamline the process, making your jobs more visible to potential applicants.
How to Create and Submit XML Sitemaps for Jobs
An XML sitemap for jobs is a specially formatted file that lists your job postings in a way that search engines can easily process. Unlike general sitemaps, these are tailored for job listings and include extra details like job titles, descriptions, locations, salaries, and posting dates. This additional information helps Google prioritize your job listings for display in Google for Jobs.
To create a job-specific XML sitemap, start by structuring your file in XML format with a <urlset> root element. Each job listing should be enclosed in a <url> tag, which includes key details such as the job's URL, the last modification date (<lastmod>), and how often the page changes (<changefreq>). Additionally, include job-specific metadata like <job:job_title>, <job:location>, <job:company_name>, <job:posting_date>, and <job:expiration_date>.
Here’s an example of how a job entry might look in your sitemap:
<url>
<loc>https://yoursite.com/jobs/software-engineer-123</loc>
<lastmod>2025-12-03</lastmod>
<job:job_title>Senior Software Engineer</job:job_title>
<job:location>San Francisco, CA</job:location>
<job:company_name>TechCorp Inc.</job:company_name>
<job:posting_date>2025-12-03</job:posting_date>
<job:expiration_date>2026-01-31</job:expiration_date>
</url>
Once your sitemap is ready, save it as sitemap-jobs.xml and upload it to your website's root directory. Depending on the size of your job board, your sitemap could include anywhere from a few dozen to tens of thousands of job entries.
To submit your sitemap to Google Search Console, start by verifying ownership of your site. Then, log in to Google Search Console, navigate to the "Sitemaps" section, and enter the full URL of your sitemap (e.g., https://yoursite.com/sitemap-jobs.xml). Click "Submit", and Google will begin processing it. Within 24 to 48 hours, you’ll see updates on whether the sitemap was successfully processed, how many URLs were indexed, and any errors that occurred.
If your submission fails, ensure your sitemap is valid XML, publicly accessible without authentication, and does not exceed 50 MB or 50,000 URLs per file. Use an online XML validator to check for errors before submission.
For job boards, it’s important to update your XML sitemap daily or whenever there are major changes, as job postings often have short lifespans. If your job board is large, consider splitting your sitemap into multiple smaller files (e.g., sitemap-jobs-1.xml, sitemap-jobs-2.xml) and creating an index file that links to all the individual sitemaps. This approach helps you stay within the 50,000 URL limit per file.
To complement your sitemap updates, use the Google Indexing API for more immediate indexing.
Using the Google Indexing API for Faster Updates
The Google Indexing API allows you to notify Google in real time whenever job listings are added, updated, or removed. Unlike XML sitemaps, which rely on Google crawling your site at its own pace, the Indexing API actively pushes updates, often leading to indexing within minutes.
To set up the Indexing API, create a Google Cloud project, enable the Indexing API, and configure OAuth 2.0 with a service account. You’ll then send HTTP POST requests to the API endpoint (https://indexing.googleapis.com/batch) with the job URLs and their notification types. Use URL_UPDATED for new or modified listings and URL_DELETED for removed jobs. Each request must include a valid OAuth 2.0 access token in the Authorization header.
By default, Google allows up to 200 requests per day per property. For job boards with high volumes of listings, use the Indexing API for urgent updates while relying on daily sitemap submissions for broader coverage.
Combining both methods ensures the best results: use sitemaps for comprehensive discovery of job listings and the Indexing API for immediate updates when time-sensitive jobs are posted or filled.
Checking Indexation Status and Fixing Problems
Use Google Search Console’s "Coverage" report to monitor how many URLs from your sitemap are indexed, excluded, or encountering errors. The report categorizes URLs as "Valid" (indexed), "Excluded" (intentionally not indexed), "Error" (indexing failed), or "Valid with warnings" (indexed but with issues).
For job-specific insights, check the "Performance" report filtered by the "Job rich results" search appearance type. This shows how many of your job listings appear in Google for Jobs search results. Additionally, use the "URL Inspection" tool to test individual job URLs for their indexation status and to identify any issues preventing indexing.
Common indexing issues include:
- "Submitted URL not found": The URL is in your sitemap, but Google can’t access it. Ensure the URL is publicly accessible, not behind login walls, and returns a 200 HTTP status code.
- "Crawled but not indexed": Google found the page but didn’t index it. Check for thin content, duplicate content, or errors in structured data implementation.
- "Noindex tag": Your job page has a noindex meta tag, preventing it from being indexed. Remove this tag to resolve the issue.
To prevent these problems, ensure your job pages are publicly accessible, contain high-quality content, and use valid JobPosting schema. Use Google’s Rich Results Test tool to validate your structured data.
Set up alerts in Google Search Console to notify you of major indexation issues or drops. Track metrics like your indexation rate (indexed URLs ÷ submitted URLs) to measure success. For job boards managing a large number of listings, platforms like Job Boardly can automate tasks like sitemap generation and Indexing API integration, allowing you to focus on growing your platform.
sbb-itb-316a34c
How to Optimize Your Google for Jobs Integration
Once you've integrated with Google for Jobs, the next step is ensuring your listings remain competitive. Indexing is just the beginning - staying visible requires keeping your data fresh and monitoring performance regularly.
Keeping Job Information Current
Keeping your job postings up-to-date is critical. Google's algorithm favors listings that are recent and relevant, while outdated postings can harm your credibility. When job seekers encounter expired listings, it not only frustrates them but also signals to Google that your site may not be reliable. This can lead to a drop in your click-through rates and potentially lower rankings for your active postings. Over time, widespread outdated content could even trigger penalties that impact your overall visibility.
To avoid this, automate the removal of expired listings after 30–60 days. This timeframe strikes a balance between keeping content fresh and providing employers with sufficient exposure. If a job is renewed or reposted, make sure to update the posting date in your schema markup. This signals Google that the listing is current, which can boost its ranking.
For job boards handling large inventories, automation is essential. Implement systems to flag jobs nearing expiration and notify employers to either renew or remove them. When a job expires, remove its JobPosting schema markup, but consider keeping the page accessible with a noindex tag for internal reference. This approach allows you to retain historical data without impacting your visibility on Google for Jobs.
Regularly updating active listings also helps. Even minor changes, such as updating application counts or adding employer notes, show Google that your site is actively maintained. This activity reinforces your authority and ensures your listings remain relevant. With your job postings in good shape, it's equally important to steer clear of common integration mistakes.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Errors in schema markup are one of the most common reasons job listings fail to appear on Google for Jobs. Missing essential fields like title, description, hiringOrganization, or jobLocation can prevent your listings from being indexed altogether.
Date formatting is another frequent issue. Google requires dates in ISO 8601 format (e.g., 2025-12-15), not the typical U.S. format like 12/15/2025. A single incorrectly formatted date can invalidate your schema markup. Similarly, salary fields must include proper currency formatting, such as "USD" for U.S. positions, and a complete baseSalary structure.
Duplicate content is a major problem for visibility. If the same job appears on multiple URLs with identical content, Google may struggle to determine which version is the authoritative one, often leading to poor rankings or removal from results. Use canonical tags (rel="canonical") to specify the primary version of a job posting when it appears on multiple URLs.
Copy-pasting job descriptions directly from employer websites can also create duplicate content issues. If you're aggregating jobs, add unique elements like company reviews, salary analysis, or location-specific insights to differentiate your listings.
Insufficient location details can hinder indexing as well. Provide precise geographic information, including the city, state, and country codes. Vague terms like "Remote" or "USA" aren't specific enough for Google to match jobs with relevant searches. For remote positions, include the company's location or specify the regions where remote work is allowed.
Finally, ensure that employment types are clearly defined using Google's accepted values: FULL_TIME, PART_TIME, CONTRACTOR, TEMPORARY, INTERN, VOLUNTEER, or PER_DIEM. Avoid custom terms or abbreviations, as Google's parser is strict about formatting and data types.
Once your listings are optimized and free from errors, you can monitor their performance through Google Search Console.
Using Google Search Console to Track Performance
Google Search Console is a powerful tool for evaluating the success of your optimization efforts. Use the "Job rich results" filter in the Performance report to track your listings' visibility.
Focus on four key metrics: impressions (how often your listings appear in search results), clicks (traffic driven to your site), click-through rate (CTR) (the percentage of impressions that lead to clicks), and average position (your listings' ranking). Job boards typically see CTRs between 2% and 8%, depending on industry and positioning. Listings in the top three positions capture about 60% to 70% of clicks, so optimizing for higher rankings is crucial.
A drop in impressions may indicate that your listings are aging out of Google's index or facing more competition. This signals a need to refresh your content or improve schema compliance. If impressions are high but CTR is low, it’s a sign that your job titles or descriptions aren’t compelling enough. Focus on making them more specific and benefit-driven to attract clicks.
The Rich Results report in Google Search Console highlights schema errors preventing proper indexing. This should be your first stop for technical troubleshooting. The report categorizes errors by severity and provides detailed guidance on what needs fixing. Addressing these issues promptly is essential, as even a small number of errors can negatively impact your site's overall quality score.
The Coverage report is another valuable resource. It identifies indexation issues across your job inventory, such as "Submitted URL not found" (indicating the URL is in your sitemap but inaccessible to Google) or "Crawled but not indexed" (suggesting Google found the page but chose not to index it due to quality concerns). Set up automated alerts to catch new issues early, and aim to maintain an indexation rate above 90% for a healthy job board.
Use the URL Inspection tool to check the indexation status of individual job URLs. This tool shows exactly what Google sees when crawling your pages, including schema markup errors or accessibility issues. After resolving any problems, request re-indexing to speed up updates.
For platforms like Job Boardly, many of these optimization tasks are streamlined with built-in features like automated schema validation, Google Indexing API integration, and compliance monitoring. These tools allow you to focus more on content quality and employer relationships and less on technical troubleshooting.
Growing Your Job Board with Proper Integration
Getting your job listings indexed on Google for Jobs is just the starting point - it’s the groundwork for long-term growth. As your job board grows from a handful of listings to hundreds or even thousands, the scalability of your setup becomes a make-or-break factor. What works for a small operation might crumble under the pressure of high-volume listings. That’s why building a scalable integration strategy from the beginning is so important - it sets the stage for steady, manageable growth.
Automating Job Data Management
Manually managing job listings is fine when you’re dealing with a small number, but it quickly becomes overwhelming as your board expands. To handle larger volumes, you’ll need automated systems that can pull job data from multiple sources - like employer submissions, API feeds, or aggregated listings - and standardize it into a consistent format.
One key element is automating the creation of JSON-LD schema for your listings. This ensures every posting meets Google’s structured data requirements. Automated checks can verify critical details, like making sure dates are in ISO 8601 format (e.g., 2025-12-15), salaries are formatted correctly in USD, and location data is precise enough for effective search matching. These steps help avoid schema errors that could stop your listings from being indexed.
Platforms such as Job Boardly simplify this process with built-in automation tools. For example, their Turbo Backfiller and Magic Aggregator tools pull in relevant job listings from various sources, cutting down on manual work. As of December 2025, these features are included in Job Boardly’s standard plans, with backfill credits costing $0.009 per API credit. This pay-as-you-go pricing gives access to over 7 million active job listings, making it easier to scale without hefty upfront expenses.
Automation doesn’t stop at creating listings - it also covers their lifecycle. Automate updates to your XML sitemaps and monitor which listings are successfully indexed. Set up workflows to remove expired jobs and prevent duplicates from multiple sources. These measures not only keep your data clean but also help maximize your indexation quota.
Once your automation is running smoothly, regular maintenance ensures your listings stay competitive and error-free.
Maintaining Visibility Over Time
Integration isn’t a “set it and forget it” process. To stay competitive, you’ll need to keep up with changes in Google’s algorithms and industry standards. One tool you can’t overlook is the Google Indexing API, which allows you to push updates directly to Google. Instead of waiting for crawlers to find changes through your XML sitemap, this API ensures new or updated listings appear in Google for Jobs much faster. But managing API quotas and meeting Google’s compliance rules requires ongoing technical oversight.
It’s also smart to diversify your traffic sources. While Google for Jobs is a powerful channel, relying on it alone can leave you vulnerable. Build direct relationships with employers and use email campaigns to drive traffic independently of search engines.
For smaller job boards, focusing on a specific niche can be more effective than trying to cover every category. Including detailed, industry-specific information in your JobPosting schema helps your listings stand out in search results for your target audience.
Staying updated with Google’s guidelines is a must. Regularly check Google Search Central for new recommendations, and use Search Console to identify indexation errors or other issues. When Google updates its structured data requirements, make adjustments quickly to avoid losing visibility.
Finally, conduct regular audits to ensure your integration is running smoothly. Use tools like Google Search Console to check for errors, monitor performance metrics (like click-through rates and impressions), verify that your XML sitemaps are updating correctly, and test a sample of job listings for valid structured data. Proactive monitoring helps you catch problems early, keeping your job board competitive and visible over time.
Conclusion
If you're looking for a "Google Jobs API", here's the reality: that product is no longer available. But don't worry - there are two reliable ways to get your job listings onto Google for Jobs: structured data using JSON-LD and XML sitemaps combined with the Google Indexing API. These approaches ensure your job postings are indexed accurately and efficiently.
Structured data helps Google understand the critical details of your job listings - like titles, locations, salaries, and URLs - in a format it can easily process. This precision improves how well your listings match relevant search queries. Meanwhile, XML sitemaps paired with the Indexing API ensure your jobs are indexed quickly, preventing delays that could cost you visibility.
When implemented correctly, these methods expand your reach. Candidates searching for jobs in your niche will see complete and accurate details, click through to your site, and apply. In contrast, poor implementation can leave your listings incomplete or, worse, invisible.
For job boards with frequent updates or large volumes of postings, combining these methods isn't just helpful - it's critical. The Indexing API is especially useful for high-volume boards, as it prevents delays that could leave your newest listings buried when they're most relevant.
To maintain strong visibility, it's crucial to keep your job data updated and monitor performance using tools like Google Search Console. By doing so, you can maximize your reach without relying entirely on paid ads or brand recognition. This is a significant advantage in a space where larger platforms often dominate.
Ultimately, structured data and XML sitemaps with the Indexing API form the foundation of your Google for Jobs strategy. Whether you're managing a small niche job board or handling thousands of listings, these tools give you the same search visibility as bigger competitors - provided you implement them correctly and keep your data accurate and up to date.
FAQs
Why did Google stop offering the Jobs API, and what does it mean for job boards and employers?
Google has phased out its Jobs API, redirecting its focus to tools like Google for Jobs, which allows users to discover job listings directly through Google Search. This means job boards and employers can no longer rely on the API for direct integration with Google's platform.
But don’t worry - your job listings can still appear on Google for Jobs. You can achieve this by either adding structured data (JSON-LD) to your job postings or submitting your job pages through sitemaps or the Indexing API. These methods ensure your listings remain accessible to job seekers using Google Search, even without the Jobs API.
How can I keep my job listings competitive and visible on Google for Jobs?
To make your job listings competitive and visible on Google for Jobs, focus on structured data, such as JSON-LD, to help search engines understand your postings. Keeping them updated is equally important to maintain their relevance and ranking.
It's also a good idea to use tools that support SEO optimization and job backfilling. These can ensure your listings remain prominent and aligned with search trends.
Don’t forget to regularly review your job postings. Make sure they include clear job descriptions, precise location details, and well-chosen keywords. Staying on top of these updates can give your listings an edge in search results.
What mistakes should I avoid when using structured data and XML sitemaps for job postings?
When working with structured data and XML sitemaps for job postings, there are a few pitfalls you’ll want to steer clear of. First, make sure your structured data is properly implemented and aligns with Google’s guidelines. Mistakes like missing required fields, using the wrong formatting, or relying on outdated schema versions can stop your job postings from showing up on Google for Jobs. Second, don’t submit incomplete or duplicate job listings in your sitemap. These issues can hurt your indexing and reduce your visibility. Finally, keep your job postings up to date. Outdated or expired listings can lead to penalties or even removal from search results.
To stay on top of things, regularly validate your structured data with tools like Google’s Rich Results Test. Also, keep an eye on your sitemap for errors using Google Search Console to ensure everything runs smoothly.